Create Operation
About
This operation allows your admins to add new entries to a database table.
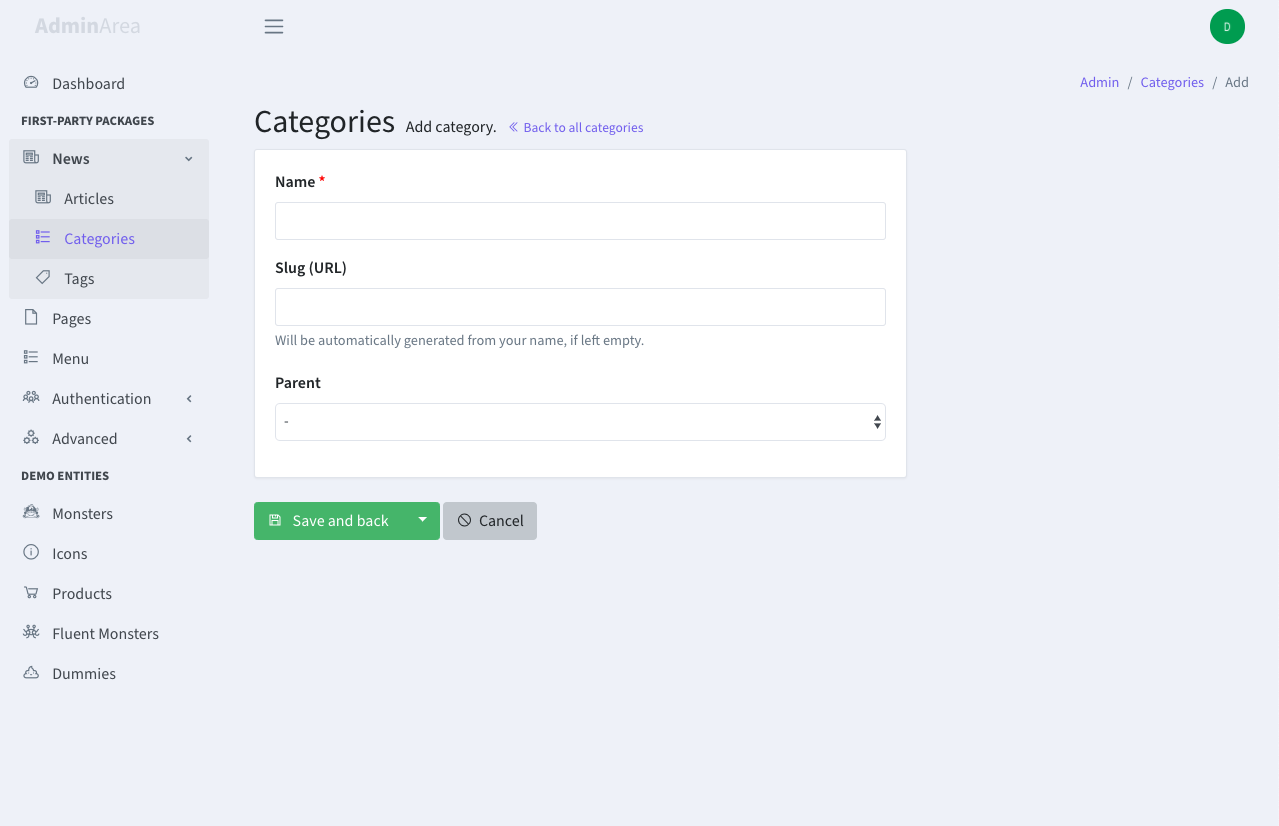
Requirements
All editable attributes should be $fillable on your Model.
How to Use
To use the Create operation, you must:
Step 0. Use the operation trait on your EntityCrudController. This should be as simple as this:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\Admin;
use Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\CrudController;
class ProductCrudController extends CrudController
{
use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\CreateOperation;
protected function setupCreateOperation()
{
// $this->crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);
// $this->crud->addField($field_definition_array);
}
}Step 1. Specify what field types you'd like to show for each editable attribute, in your EntityCrudController's setupCreateOperation() method. You can do that using the Fields API. In short you can:
protected function setupCreateOperation()
{
$this->crud->addField($field_definition_array);
}Step 2. Specify validation rules, in your the EntityCrudRequest file. Then make sure that file is used for validation, by telling the CRUD to validate that request file in setupCreateOperation():
$this->crud->setValidation(StoreRequest::class);For more on how to manipulate fields, please read the Fields documentation page. For more on validation rules, check out Laravel's validation docs.
How It Works
CrudController is a RESTful controller, so the Create operation uses two routes:
- GET to
/entity-name/create- points tocreate()which shows the Add New Entry form (create.blade.php); - POST to
/entity-name- points tostore()which does the actual storing operation;
The create() method will show all the fields you've defined for this operation using the Fields API, then upon Save the store() method will first check the validation from the FormRequest you've specified, then create the entry using the Eloquent model. Only attributes that are specified as fields, and are $fillable on the model will actually be stored in the database.
Callbacks
Developers coming from GroceryCRUD or other CRUD systems will be looking for callbacks to run before_insert, before_update, after_insert, after_update. There are no callbacks in Backpack. The store code is inside a trait, so you can easily overwrite it:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\Admin;
use Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\CrudController;
class ProductCrudController extends CrudController
{
use \Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\Operations\CreateOperation { store as traitStore; }
// ...
public function store()
{
// do something before validation, before save, before everything; for example:
// $this->crud->addField(['type' => 'hidden', 'name' => 'author_id']);
// $this->crud->removeField('password_confirmation');
// Note: By default Backpack ONLY saves the inputs that were added on page using Backpack fields.
// This is done by stripping the request of all inputs that do NOT match Backpack fields for this
// particular operation. This is an added security layer, to protect your database from malicious
// users who could theoretically add inputs using DeveloperTools or JavaScript. If you're not properly
// using $guarded or $fillable on your model, malicious inputs could get you into trouble.
// However, if you know you have proper $guarded or $fillable on your model, and you want to manipulate
// the request directly to add or remove request parameters, you can also do that.
// We have a config value you can set, either inside your operation in `config/backpack/crud.php` if
// you want it to apply to all CRUDs, or inside a particular CrudController:
// $this->crud->setOperationSetting('saveAllInputsExcept', ['_token', '_method', 'http_referrer', 'current_tab', 'save_action']);
// The above will make Backpack store all inputs EXCEPT for the ones it uses for various features.
// So you can manipulate the request and add any request variable you'd like.
// $this->crud->getRequest()->request->add(['author_id'=> backpack_user()->id]);
// $this->crud->getRequest()->request->remove('password_confirmation');
$response = $this->traitStore();
// do something after save
return $response;
}
}But before you do that, ask yourself - is this something that should be done when an entry is added/updated/deleted from the application, too? Not just the admin panel? If so, a better place for it would be the Model. Remember your Model is a pure Eloquent Model, so the cleanest way might be to use Eloquent Event Observers or accessors and mutators.
Translatable models and multi-language CRUDs
For UX purposes, when creating multi-language entries, the Create form will only allow the admin to add an entry in one language, the default one. The admin can then edit that entry in all available languages, to translate it. Check out this same section in the Update operation for how to enable multi-language functionality.
Separate Validation Rules for Create and Update
Differences between the Create and Update validations? If your Update operation requires a different validation than the Create operation, just:
- create a separate request file for each operation;
- instruct your EntityCrudController to use separate files, in the "use" section;
For example, we could create UpdateTagRequest.php and CreateTagRequest.php, with different validations, then in TagCrudController just do:
- use App\Http\Requests\TagRequest as StoreRequest;
+ use App\Http\Requests\CreateTagRequest as StoreRequest;
- use App\Http\Requests\TagRequest as UpdateRequest;
+ use App\Http\Requests\UpdateTagRequest as UpdateRequest;