2. CRUD Operations
Duration: 10 minutes
Let's bring back the example in our first lesson. The Tags CRUD:
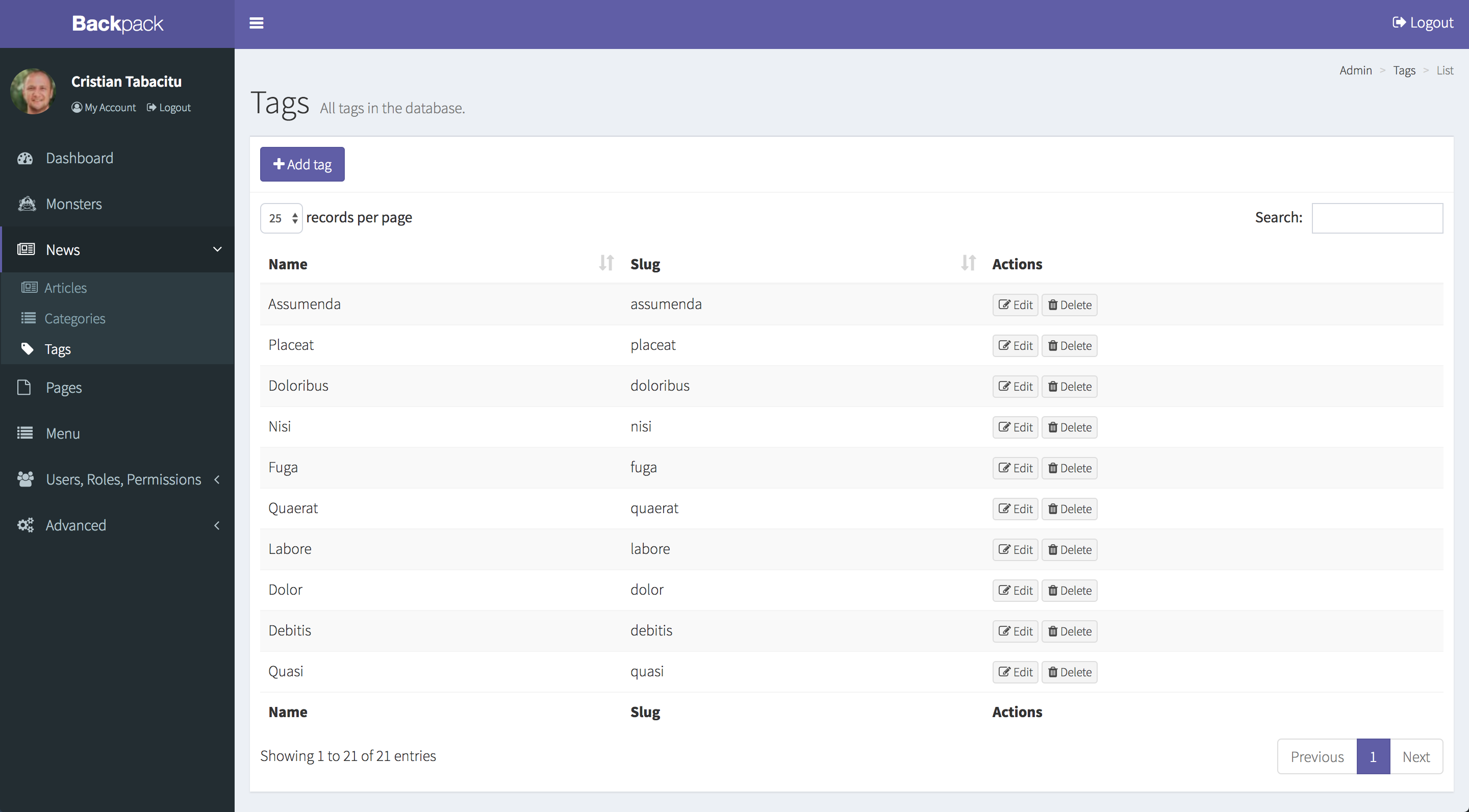
With its TagCrudController:
<?php namespace App\Http\Controllers\Admin;
use Backpack\CRUD\app\Http\Controllers\CrudController;
// VALIDATION: change the requests to match your own file names if you need form validation
use App\Http\Requests\TagCrudRequest as StoreRequest;
use App\Http\Requests\TagCrudRequest as UpdateRequest;
class TagCrudController extends CrudController {
public function setup()
{
$this->crud->setModel("App\Models\Tag");
$this->crud->setRoute("admin/tag");
$this->crud->setEntityNameStrings('tag', 'tags');
$this->crud->setColumns(['name', 'slug']);
$this->crud->addField([
'name' => 'name',
'type' => 'text',
'label' => "Tag name"
]);
$this->crud->addField([
'name' => 'slug',
'type' => 'text',
'label' => "URL Segment (slug)"
]);
}
public function store(StoreRequest $request)
{
return parent::storeCrud();
}
public function update(UpdateRequest $request)
{
return parent::updateCrud();
}
}By default, CRUDs have these operations already enabled:
- Create - using a create form (aka "add form")
- ListEntries - using AJAX DataTables (aka "list view", aka "table view")
- Update - using an update form (aka "edit form")
- Delete - using a button in the list view
These are the basic operations an admin can execute on an Eloquent model, thanks to Backpack. We do have additional operations (Preview, Reorder, Revisions), and you can easily create a custom operation, but let's not get ahead of ourselves. Baby steps. Let's go through the most important features of the operations you'll be using all the time: ListEntries, Create and Update.
Create & Update Operations
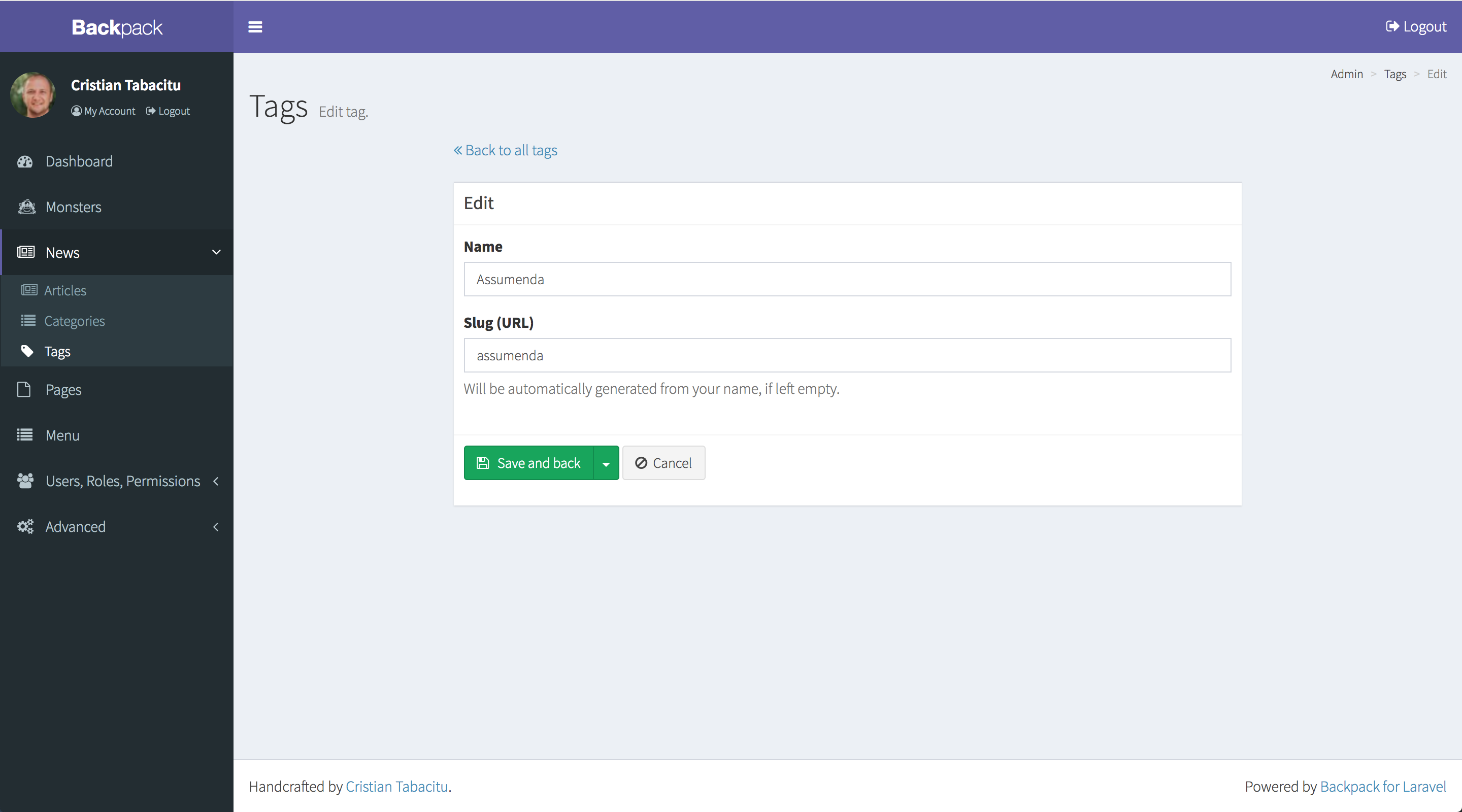
Fields
Inside your Controller's setup() method, you'll be able to define what fields you want the admin to see, when creating/updating entries. In the example above, we only have two fields, both using the text field type. So that's what's shown to the admin. When the admin presses Save, assuming your model has those two attributes as $fillable, Backpack will save the entry and take you back to the ListEntries view. Keep in mind we're using a pure Eloquent model. So of course, inside the model you could use accessors, mutators, events, etc.
But a lot of times, you won't just need text inputs. You'll need datepickers, upload buttons, 1-n relationship, n-n relationships, textareas, etc. For each field, you only need to define it properly in the Controller's setup() method. Here are the most used methods to manipulate fields:
// You can pass a second parameter with the operation:
// - "create" for Create
// - "update" for Update
// - nothing (missing) for both Create and Update
$this->crud->addField($field_definition_array);
$this->crud->addFields([$field_definition_array_1, $field_definition_array_2]);
$this->crud->removeField('name');
$this->crud->removeFields(['name_1', 'name_2']);
// pro tip:
// a quick way to add simple fields: let the CRUD decide what field type it is
$this->crud->addField('db_column_name'); A typical field definition array will need at least three things:
name- the attribute (column in the database), which will also become the name of the input;type- the kind of field we'd like to use (text, number, select2, etc);label- the human-readable label for the input (will be generated fromnameif not given);
You can use one of the 44+ field types we've provided, or easily create a custom field type if you have some super-specific need that we haven't covered yet, or even overwrite how a field type works. Take a few minutes and browse the 44+ field types, to understand how the definition array differs from one to another and how many use cases you have already covered.
Let's take another example, slightly more complicated than the text fields we used above. Something you'll find encounter all the time is relationship fields. So let's say the Tag model has an n-n relationship with an Article model:
public function articles()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Article', 'article_tag');
}We could use the code below to add a select2_multiple field to the Tag update forms:
$this->crud->addField([
'label' => "Articles",
'type' => 'select2_multiple',
'name' => 'articles', // the relationship name in your Model
'entity' => 'articles', // the relationship name in your Model
'attribute' => 'title', // attribute on Article that is shown to admin
'pivot' => true, // on create&update, do you need to add/delete pivot table entries?
], 'update');Notes:
- Because of the last parameter ("update"), the field will only be added on the Update form (not on the Create);
- Because we haven't specified a
label, Backpack will take the "articles" name and turn it into a label: "Articles";
If we had an Articles CRUD, and the reverse relationship defined on the Article model too, we could also add a select2_multiple field in the Article CRUD, to allow the admin to choose which tags apply to each article. This actually makes more sense than the above :-)
$this->crud->addField([
'label' => "Tags",
'type' => 'select2_multiple',
'name' => 'tags', // the method that defines the relationship in your Model
'entity' => 'tags', // the method that defines the relationship in your Model
'attribute' => 'name', // foreign key attribute that is shown to user
'pivot' => true, // on create&update, do you need to add/delete pivot table entries?
]);Note: Because the last parameter is missing, the field will be added to both Create and Update forms.
When generating a CrudController, you'll be using the
$this->crud->setFromDb();method by default, which tries to figure out what fields you might need in your create/update forms and in your list view, but - as you'd expect - only works for the simple field types. You can:(1) choose to keep using
setFromDb()and add/remove/change additional fieldsor
(2) delete
setFromDb()and manually define each field and column;Our recommendation, for anything but the simplest CRUDs, is to manually define each field - much easier to understand and customize, for your future self and any other developer that comes after you.
Callbacks
Developers coming from GroceryCRUD on CodeIgniter or other CRUD systems will be looking for callbacks to run before_insert, before_update, after_insert, after_update.
There are no callbacks in Backpack, because there's no need. The code for the create & update operations is out in the open for you to customize. Notice your EntityCrudController already has the following methods, which you can modify as you wish:
public function store(StoreRequest $request)
{
// <--------- here is where a before_insert callback logic would be
$response = parent::storeCrud();
// <--------- here is where a after_insert callback logic would be
return $response;
}
public function update(UpdateRequest $request)
{
// <--------- here is where a before_update callback logic would be
$response = parent::updateCrud();
// <--------- here is where a after_update callback logic would be
return $response;
}But before you do that, ask yourself - is this something that should be done when an entry is added/updated/deleted from the application, too? Not just the admin admin? If so, a better place for it would be the Model. Remember your Model is a pure Eloquent Model, so the cleanest way might be to use Eloquent Event Observers or accessors and mutators.
ListEntries Operation
ListEntries shows the admin a table with all entries. On the front-end, the information is pulled using AJAX calls, and shown using DataTables. It's the most feature-packed operation in Backpack, but right now we're just going through the most important features you need to know about: columns, filters and buttons.
Columns
Columns help you specify which attributes are shown in the table and in which order. They're defined in the setup() method, the same as fields, and their syntax is super-similar to fields too:
$this->crud->addColumn($column_definition_array); // add a single column, at the end of the table
$this->crud->addColumns([$column_definition_array_1, $column_definition_array_2]); // add multiple columns, at the end of the table
$this->crud->removeColumn('column_name'); // remove a column from the table
$this->crud->removeColumns(['column_name_1', 'column_name_2']); // remove an array of columns from the table
$this->crud->setColumnDetails('column_name', ['attribute' => 'value']);
$this->crud->setColumnsDetails(['column_1', 'column_2'], ['attribute' => 'value']);
$this->crud->setColumns([$column_definition_array_1, $column_definition_array_2]); // make these the only columns in the tableYou can use one of the 14+ column types to show information to the user in the table, or easily create a custom column type, if you have a super-specific need. Here's an example of using the methods above:
$this->crud->addColumn([
'name' => 'published_at',
'type' => 'date',
'label' => 'Publish_date',
]);
// PRO TIP: to quickly add a text column, just pass the name string instead of an array
$this->crud->addColumn('text'); // adds a text column, at the end of the stackFilters
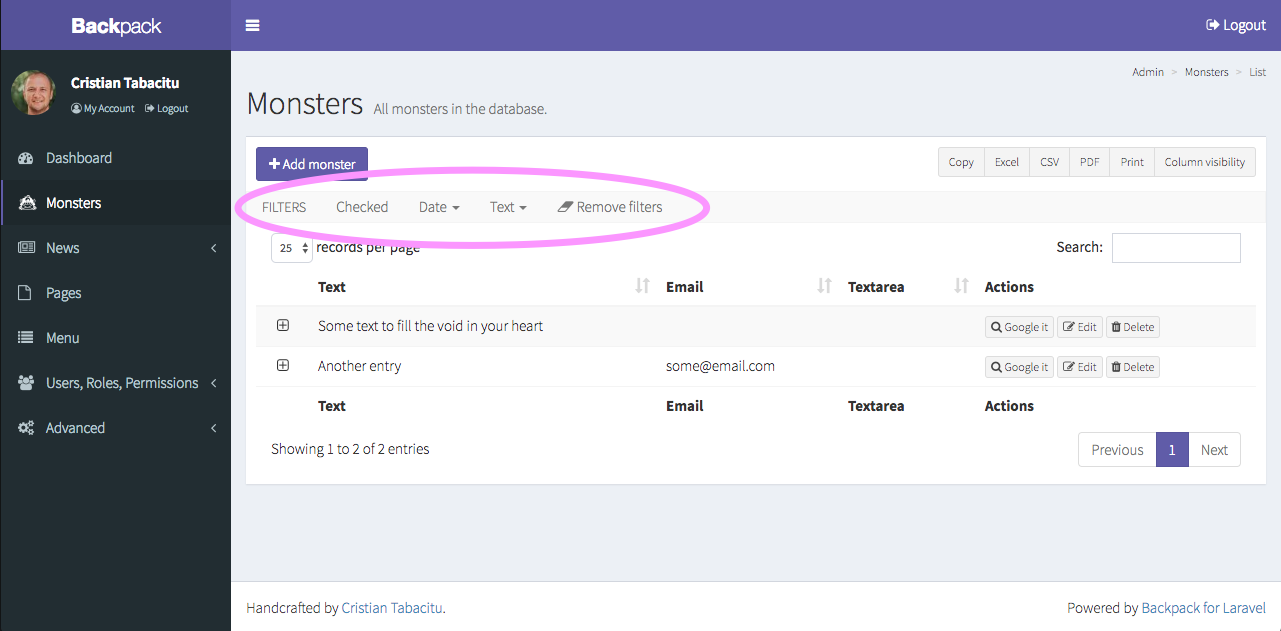
Filters provide an easy way for the admin to well… filter the ListEntries table. The syntax is very similar to Fields and Columns and you can use one of the existing 8 filter types or easily create a custom filter.
$this->crud->addFilter($options, $values, $filter_logic);
$this->crud->removeFilter($name);
$this->crud->removeAllFilters();For more on this, check out the filters documentation page, when you need them.
Buttons
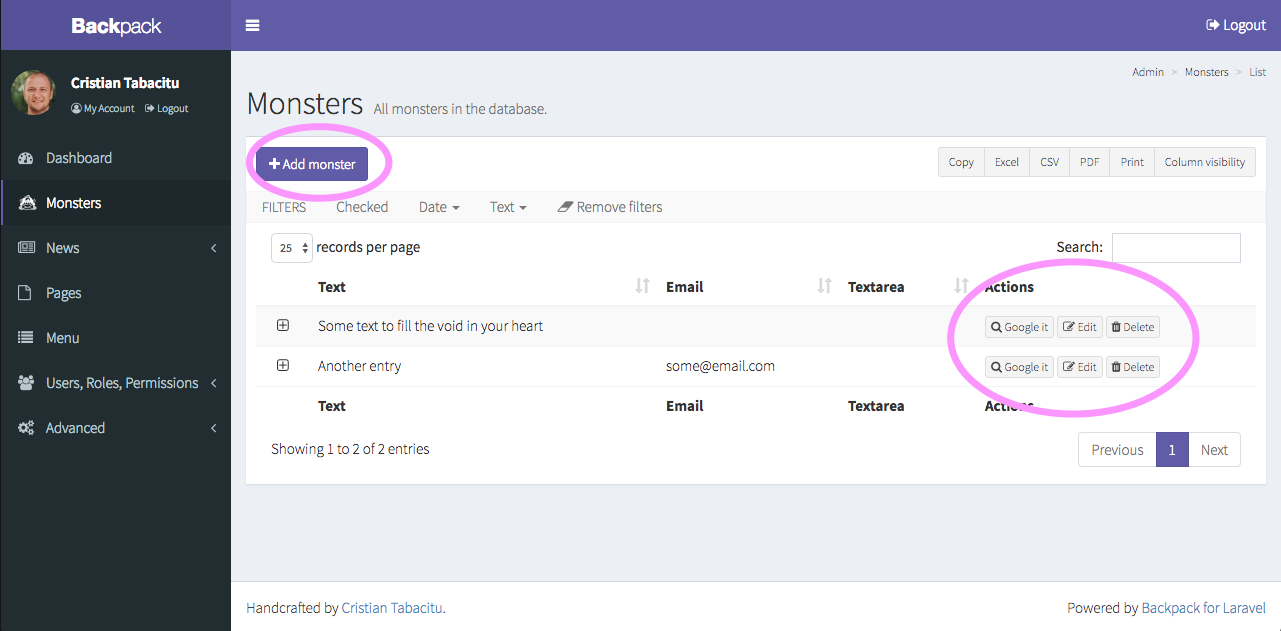
If you want to add a custom button to an entry, you can do that. If you want to remove a button, you can also do that. Look for the buttons documentation when you need it.
// positions: 'beginning' and 'end'
// stacks: 'line', 'top', 'bottom'
// types: view, model_function
$this->crud->addButton($stack, $name, $type, $content, $position);
$this->crud->removeButton($name);
$this->crud->removeButtonFromStack($name, $stack);That's it for today! Thanks for sticking with us this long. This has been the most important and longest lesson. You can go ahead and install Backpack now, as you've already gone through the most important features. Or read the next lesson, about advanced features.